Chart of Careers In Plant-Based and Cultivated Meat
An infographic of the Good Food Institute's research
The Good Food Institute’s student guide lists which fields of research allow you to work on which aspects of developing better plant-based or cultivated meat. Unfortunately, it’s a little hard to read, so I and my friend Elena Churilov collaborated on this graphic:
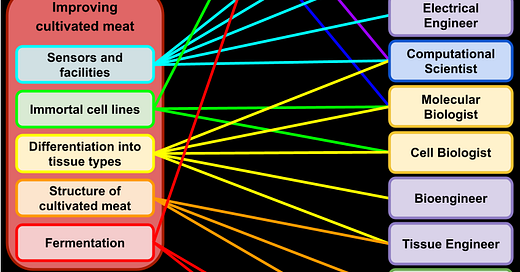
On the left, the green means that this is a component of improving plant-based meat; the red, that this is a component of improving cultivated meat. On the right, purple indicates an engineering field; yellow, microbiology; green, biology that is not microbiology; and blue, other fields.
Areas of Research In Plant-Based and Cultivated Meat
In plant-based meat, making plants better raw materials means optimizing plants we’re familiar with to make them better materials for plant-based meat, such as by making them higher protein or tastier. Predicting the right plants means creating a model which lets us identify which plants (perhaps even ones we don’t eat right now) could have applications in plant-based meat—before we do expensive and time-consuming research. Going from plants to ingredients means studying how to take a plant and break it down into the best raw materials to construct plant-based meat. Texture and mouthfeel means figuring out how to produce the best texture and mouthfeel from a particular set of ingredients.
In cultivated meat, sensors and facilities means designing factories for cultivated meat. Immortal cell lines means making stem cells that can divide indefinitely, without any limit. Differentiation into tissue types means getting stem cells to transform into the desired cell type at an industrial scale rather than a lab scale. Structure of cultivated meat means researching how to create complex cuts of meat like a T-bone steak. Fermentation means developing ingredients for plant-based and cultivated meat using algae, fungi, bacteria, and other single-celled microbe sources
Careers
Mechanical engineers build mechanical and thermal sensors, tools, engines, and machines, from medical devices to internal combustion engines. Genetic engineers directly modify the genetic makeup of cells. Chemical engineers work with chemicals to produce drugs, fuel, food, and other products. Bioengineers work with biological systems and biomedical technologies to create everything from medical imaging technology to engineered organs. Tissue engineers are a kind of bioengineer who focus on constructing, maintaining, repairing, and replacing biological tissues. Electrical engineers build electrical equipment, from electric motors to radar systems. Industrial biotechnologists research the use of biological systems—from individual enzymes to entire plants—in industrial processes.
Biochemists study the chemical principles of living organisms and biological processes like growth and development. Molecular biologists are a kind of biochemist who studies how cells work on a molecular level. Cell biologists are a kind of biochemist who studies the structure, function, and organization of cells. Microbiologists study microorganisms: fungi, bacteria, viruses, algae, and some parasites.
Plant scientists work in the agricultural sector to control weeds and pests and improve crop yields. Plant biologists study plants from an academic perspective. Food scientists study the basic components of food, from nutrition to taste. Mycologists study fungi. Meat scientists study all aspects of meat, from animal growth to processing meat products.
Data scientists analyze and draw conclusions from data. Computational scientists use advanced computing capabilities to develop models that help us understand complex systems. Designers create plans for something before it is made (in this case, the sensors and facilities needed to produce cultivated meat).



https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/vegan-spider-silk-provides-sustainable-alternative-to-single-use-plastics
A little sideways from your topic, but it's synthetic manufacture of an animal product.
Awesome post! Too bad I am only one person and cannot have six careers.